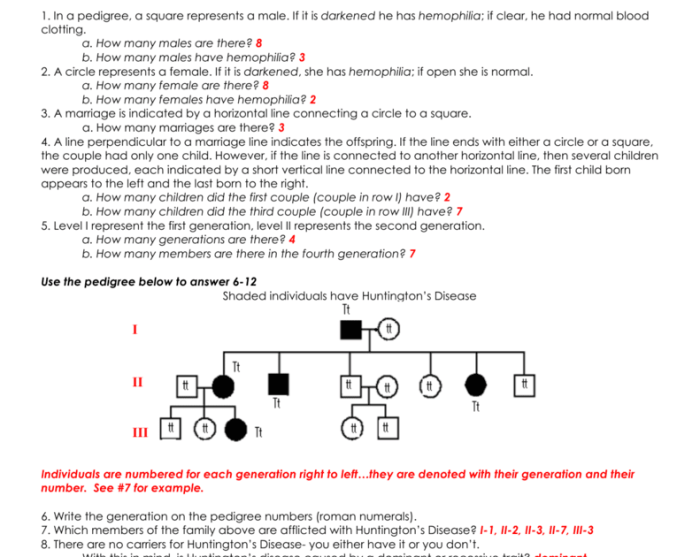
Pedigree charts worksheet answer key provides a comprehensive guide to understanding the fundamentals of pedigree charts, empowering individuals to decipher the intricate patterns of inheritance. Through this resource, users will gain insights into the symbols, analysis, and applications of pedigree charts, enabling them to effectively interpret genetic information.
Pedigree charts serve as invaluable tools in various fields, including medical genetics, animal breeding, and evolutionary biology. By studying the inheritance patterns within families, researchers can identify genetic disorders, predict disease risks, and trace the evolution of species. However, it is essential to acknowledge the limitations of pedigree charts and approach their interpretation with caution, considering the potential for incomplete data and complex inheritance patterns.
Introduction
Pedigree charts are diagrams that depict the inheritance of traits in a family over multiple generations. They are used to study the patterns of inheritance and to identify the mode of transmission of genetic disorders.
Pedigree charts are important because they allow researchers to:
- Determine the mode of inheritance of a trait.
- Identify carriers of genetic disorders.
- Predict the risk of developing a genetic disorder in future generations.
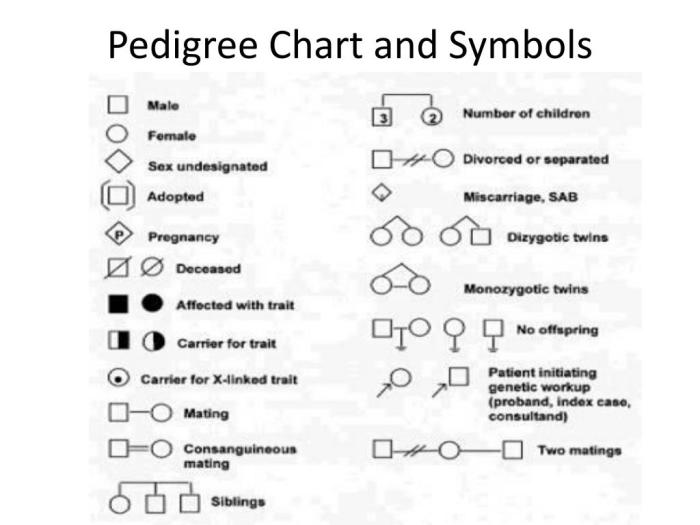
Understanding Pedigree Chart Symbols
Pedigree charts are valuable tools in genetic counseling and medical research. They provide a visual representation of the inheritance patterns of traits within a family. Understanding the symbols used in pedigree charts is essential for accurately interpreting and analyzing these charts.
The following is a comprehensive list of symbols commonly used in pedigree charts, along with their meanings and examples:
Male and Female Symbols
- Square:Represents a male individual.
- Circle:Represents a female individual.
Status of Individuals
- Solid Symbol:Represents an individual who is affected by the trait being studied.
- Open Symbol:Represents an individual who is not affected by the trait being studied.
- Half-shaded Symbol:Represents an individual who is a carrier of the trait but does not exhibit its symptoms.
- Striped Symbol:Represents an individual who is deceased.
Relationships
- Horizontal Line:Represents a marriage or partnership.
- Vertical Line:Represents the offspring of a marriage or partnership.
- Brackets:Connect individuals who have had children together.
- Double Line:Represents identical twins.
- Single Line:Represents fraternal twins.
Additional Symbols
- Arrow:Points to the individual who is the proband (the person who initially presented with the trait being studied).
- Asterisk (*):Indicates that an individual has been tested and found to have a specific genetic mutation.
- Plus Sign (+):Indicates that an individual has been tested and found to be unaffected by a specific genetic mutation.
These symbols provide a standardized way to represent the inheritance patterns of traits within a family. By understanding their meanings, researchers and clinicians can effectively interpret and analyze pedigree charts to gain valuable insights into the genetic basis of traits and diseases.
Analyzing Pedigree Charts: Pedigree Charts Worksheet Answer Key
Analyzing pedigree charts involves examining the patterns of inheritance within a family to determine the mode of inheritance of a particular trait or condition.
Identifying Inheritance Patterns
Pedigree charts can be used to identify the inheritance patterns of traits, such as dominant, recessive, and sex-linked traits.
Dominant Traits
- Expressed in individuals who inherit at least one copy of the dominant allele.
- Represented by filled symbols in pedigree charts.
- Example: Brown eye color
Recessive Traits
- Expressed only in individuals who inherit two copies of the recessive allele.
- Represented by open symbols in pedigree charts.
- Example: Blue eye color
Sex-linked Traits
- Traits whose genes are located on the X or Y chromosomes.
- More commonly expressed in males than females.
- Example: Red-green colorblindness
Creating Pedigree Charts
Creating pedigree charts involves using specific software or online tools to visually represent family relationships and genetic traits. These charts play a crucial role in genetic counseling, medical research, and tracing the inheritance patterns of specific traits or diseases within families.
Best Practices for Creating Clear and Accurate Pedigree Charts
To create clear and accurate pedigree charts, it is essential to adhere to the following best practices:
- Use standard symbols:Employ universally recognized symbols to represent individuals, relationships, and genetic traits, ensuring consistency and clarity.
- Maintain consistency:Utilize the same symbols and conventions throughout the chart to avoid confusion and facilitate easy interpretation.
- Provide sufficient information:Include essential details such as names, dates of birth, and relevant medical information to provide context and enable accurate analysis.
- Organize information logically:Arrange individuals within the chart based on their familial relationships, using a clear and hierarchical structure.
- Use clear and concise labeling:Label all symbols and relationships explicitly to enhance understanding and avoid ambiguity.
Examples of Well-Designed Pedigree Charts
Well-designed pedigree charts are characterized by their clarity, accuracy, and informative value. They effectively convey genetic information and family relationships in a visually accessible manner.
- Pedigree Chart for a Family with Huntington’s Disease:This chart illustrates the inheritance pattern of Huntington’s disease, an autosomal dominant disorder. It clearly depicts the affected individuals and their relationships, highlighting the mode of inheritance.
- Pedigree Chart for a Family with Cystic Fibrosis:This chart demonstrates the inheritance of cystic fibrosis, an autosomal recessive disorder. It shows the carriers and affected individuals, providing valuable information for genetic counseling and family planning.
Applications of Pedigree Charts
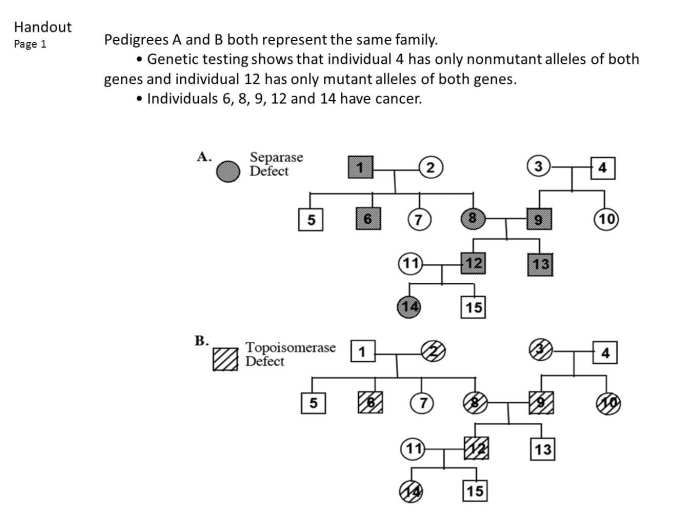
Pedigree charts have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
Medical Genetics
In medical genetics, pedigree charts are used to:
- Identify patterns of inheritance for genetic disorders
- Determine the risk of an individual inheriting a particular disorder
- Plan for genetic counseling and family planning
For example, a pedigree chart can be used to track the inheritance of a recessive disorder like cystic fibrosis. By examining the pattern of inheritance in the family, a genetic counselor can determine the likelihood of an individual carrying the recessive allele and the risk of having an affected child.
Animal Breeding
In animal breeding, pedigree charts are used to:
- Maintain genetic diversity and prevent inbreeding
- Identify desirable traits and select animals for breeding
- Track the lineage and genetic history of animals
For example, a pedigree chart can be used to track the lineage of a champion racehorse. By examining the pedigree, breeders can identify the ancestors that contributed to the horse’s exceptional performance and select breeding partners that will maintain or enhance those traits.
Evolutionary Biology, Pedigree charts worksheet answer key
In evolutionary biology, pedigree charts are used to:
- Study the evolution of genetic traits
- Trace the genetic relationships between different populations
- Understand the genetic basis of adaptation and speciation
For example, a pedigree chart can be used to study the evolution of beak shape in Darwin’s finches. By examining the pedigree of finches from different islands, researchers can determine how beak shape has changed over time and how it has contributed to the speciation of different finch populations.
Limitations of Pedigree Charts
Pedigree charts are valuable tools for studying inheritance patterns, but they also have certain limitations.
One limitation is that pedigree charts can only show a limited number of generations. This can make it difficult to identify patterns of inheritance that span multiple generations. Additionally, pedigree charts can only show relationships between individuals who are related through blood or marriage.
This can make it difficult to identify relationships between individuals who are related through adoption or other non-genetic means.
Another limitation of pedigree charts is that they can be incomplete. This can happen for a variety of reasons, such as when individuals are not aware of their family history or when information about family members is not available. Incomplete pedigree charts can make it difficult to draw accurate conclusions about inheritance patterns.
Finally, pedigree charts can be difficult to interpret when inheritance patterns are complex. This can happen when multiple genes are involved in a trait or when the inheritance pattern is not clear. Complex inheritance patterns can make it difficult to determine the risk of inheriting a particular trait.
Interpreting Pedigree Charts with Caution
Given the limitations of pedigree charts, it is important to interpret them with caution. When interpreting a pedigree chart, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The completeness of the chart
- The number of generations shown
- The complexity of the inheritance pattern
It is also important to consider other sources of information when interpreting a pedigree chart. These sources can include medical records, genetic testing, and family history interviews.
FAQ Overview
What are pedigree charts used for?
Pedigree charts are used to represent the inheritance patterns of traits within families, helping researchers identify genetic disorders, predict disease risks, and trace the evolution of species.
How do I analyze a pedigree chart?
Pedigree chart analysis involves identifying the symbols representing individuals, their relationships, and the traits being studied. By examining the patterns of inheritance, researchers can determine the mode of inheritance (dominant, recessive, sex-linked) and identify carriers or affected individuals.
What are the limitations of pedigree charts?
Pedigree charts may have limitations due to incomplete data or complex inheritance patterns. It is essential to interpret pedigree charts with caution and consider other sources of information, such as genetic testing, to obtain a comprehensive understanding of genetic traits.