Crop gap ap human geography definition – In the realm of human geography, the crop gap—a discrepancy between the potential and actual agricultural production—emerges as a multifaceted phenomenon with profound implications for global food security, economic stability, and environmental sustainability.
This introductory paragraph provides a comprehensive overview of the topic, highlighting the significance of crop gaps and their far-reaching consequences.
Definition of Crop Gap

In human geography, a crop gap refers to the difference between the potential crop yield in a given region and the actual yield obtained. This gap can manifest in different ways, such as the shortfall in production to meet local demand or the disparity between potential and actual yields due to various constraints.
Causes of Crop Gaps

The major causes of crop gaps include:
- Climatic factors: Adverse weather conditions, such as droughts, floods, or extreme temperatures, can significantly reduce crop yields.
- Soil conditions: Poor soil quality, nutrient deficiencies, or salinity can limit crop growth and productivity.
- Technological limitations: Lack of access to improved seeds, fertilizers, or irrigation systems can hinder crop production.
Consequences of Crop Gaps
Crop gaps have severe consequences, including:
- Food insecurity: Crop shortfalls can lead to food shortages and malnutrition.
- Economic losses: Reduced crop production can result in financial losses for farmers and the economy as a whole.
- Environmental degradation: Intensive farming practices to bridge crop gaps can lead to soil erosion, water pollution, and deforestation.
Strategies to Reduce Crop Gaps
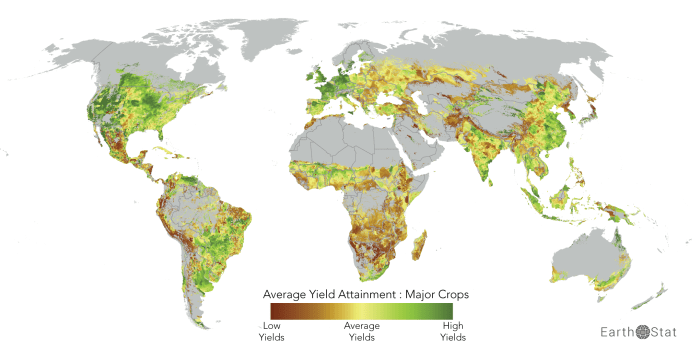
Strategies to reduce crop gaps include:
- Improved agricultural practices: Sustainable farming techniques, such as crop rotation, conservation tillage, and precision agriculture, can enhance crop yields.
- Technological advancements: Innovations in seed technology, irrigation systems, and mechanization can increase crop productivity.
- Policy interventions: Government policies that promote agricultural research, provide incentives for sustainable farming, and address market failures can help reduce crop gaps.
Answers to Common Questions: Crop Gap Ap Human Geography Definition
What is the definition of a crop gap in human geography?
A crop gap refers to the difference between the potential crop yield that could be achieved under optimal conditions and the actual yield obtained due to various limiting factors.
What are the major causes of crop gaps?
Crop gaps can result from a combination of factors, including climatic conditions, soil quality, water availability, technological limitations, and socioeconomic constraints.
What are the consequences of crop gaps?
Crop gaps can lead to food insecurity, economic losses for farmers, and environmental degradation due to unsustainable agricultural practices.
What strategies can be implemented to reduce crop gaps?
Strategies to reduce crop gaps include improving agricultural practices, adopting new technologies, implementing sustainable land management practices, and addressing socioeconomic factors that affect agricultural productivity.