Which scenario matches the homeostasis strategy of kleptothermy? Kleptothermy, the utilization of external heat sources to regulate body temperature, is a fascinating adaptation employed by various animal species. This article delves into the intricacies of kleptothermy, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, limitations, and evolutionary significance, providing a comprehensive understanding of this unique thermoregulatory strategy.
Kleptothermy offers animals advantages such as energy conservation and extended activity range, but it also presents limitations, including dependence on external heat sources. Understanding the comparative advantages and disadvantages of kleptothermy relative to other homeostasis strategies, such as endothermy and ectothermy, is crucial for comprehending the ecological adaptations of different animal species.
Kleptothermy and Homeostasis

Kleptothermy is a behavioral and physiological strategy employed by certain animals to maintain body temperature. It involves acquiring heat from external sources, such as the sun, warm surfaces, or other animals, rather than generating it internally.
Kleptothermy plays a crucial role in homeostasis by regulating body temperature within a narrow range necessary for survival and optimal physiological function.
Mechanisms of Kleptothermy: Which Scenario Matches The Homeostasis Strategy Of Kleptothermy

Behavioral Adaptations
- Basking:Exposing the body to sunlight or warm surfaces to absorb heat.
- Huddling:Clustering together with other animals to share body heat.
- Seeking Shelter:Utilizing burrows, caves, or shaded areas to protect from extreme temperatures.
Physiological Adaptations
- Reduced Insulation:Animals with low body fat or fur have a reduced capacity to retain heat internally.
- Large Surface Area:Species with large surface-to-volume ratios facilitate heat exchange with the environment.
- Vasoconstriction and Vasodilation:Adjusting blood flow to the skin regulates heat loss and gain.
Benefits and Limitations of Kleptothermy
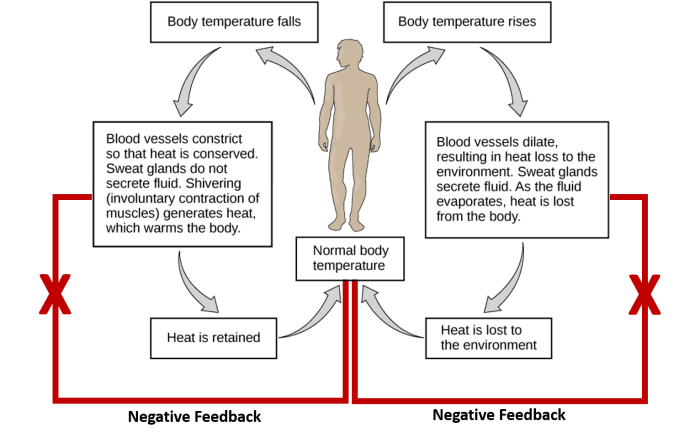
Advantages
- Energy Conservation:Kleptothermy reduces the need for metabolic heat production, conserving energy.
- Extended Activity Range:Animals can remain active during cooler periods by utilizing external heat sources.
Limitations
- Dependence on External Heat:Kleptotherms rely on external sources, which may not always be available or reliable.
- Susceptibility to Predators:Basking or huddling behaviors may make animals vulnerable to predators.
Comparative Analysis of Kleptothermy and Other Homeostasis Strategies
Endothermy
- Internal Heat Production:Generate heat through metabolic processes.
- Independent of External Heat:Maintain body temperature regardless of environmental conditions.
- High Energy Requirements:Constant heat production requires substantial energy input.
Ectothermy, Which scenario matches the homeostasis strategy of kleptothermy
- External Heat Dependence:Rely on external heat sources to regulate body temperature.
- Lower Energy Requirements:Heat is acquired passively, conserving energy.
- Limited Activity Range:Body temperature is influenced by environmental fluctuations.
Evolutionary Significance of Kleptothermy
Kleptothermy has evolved in response to environmental pressures, particularly in habitats with fluctuating or limited temperatures.
It has contributed to the survival and success of certain species by:
- Expanding Habitat Range:Enabling animals to inhabit areas with cooler climates.
- Reducing Energy Expenditure:Conserving energy for other essential functions.
- Facilitating Nocturnal Activity:Allowing animals to remain active during cooler nighttime hours.
Query Resolution
What is kleptothermy?
Kleptothermy is a thermoregulatory strategy where animals utilize external heat sources to maintain body temperature.
What are the benefits of kleptothermy?
Kleptothermy offers advantages such as energy conservation and extended activity range.
What are the limitations of kleptothermy?
Kleptothermy presents limitations, including dependence on external heat sources.