Nonnuclear submarines use batteries for power when submerged – Nonnuclear submarines employ batteries as their primary source of power when submerged, offering unique advantages and considerations compared to their nuclear-powered counterparts. This comprehensive analysis delves into the intricate details of battery functionality, technological advancements, power management strategies, operational considerations, and future trends in submarine power systems.
Batteries play a crucial role in powering nonnuclear submarines, providing the necessary energy to propel the vessel and operate auxiliary systems while submerged. These battery systems boast impressive technical specifications, including high capacity, voltage, and lifespan, ensuring reliable and sustained performance during underwater operations.
Submerged Propulsion: Battery Functionality
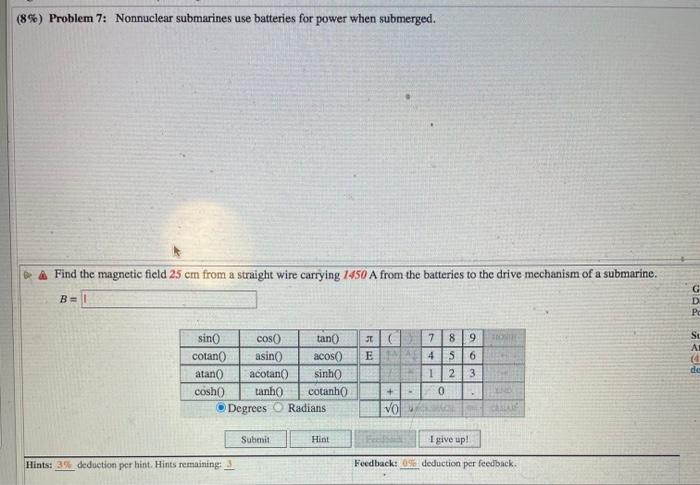
In submerged operations, nonnuclear submarines rely solely on battery power for propulsion. These batteries serve as the primary energy source, providing electricity to drive the submarine’s electric motors and auxiliary systems.
Battery systems used in nonnuclear submarines typically employ advanced technologies to maximize capacity, efficiency, and lifespan. Common battery types include lead-acid, silver-zinc, and lithium-ion batteries, each with its unique advantages and limitations.
Capacity refers to the amount of electrical energy a battery can store, measured in amp-hours (Ah). Voltage, measured in volts (V), indicates the electrical potential difference between the battery’s terminals. Lifespan, measured in cycles or years, represents the number of charge-discharge cycles or the duration over which the battery can maintain a usable capacity.
Battery Technology Advancements
Advancements in battery technology have significantly enhanced the performance of nonnuclear submarines.
- Increased Capacity:Research and development efforts have focused on developing battery materials with higher energy density, enabling batteries to store more energy in a given volume.
- Improved Efficiency:Innovations in battery design and chemistry have led to improved charge-discharge efficiency, reducing energy losses and extending the operational range of submarines.
- Extended Lifespan:Advanced battery management systems and conditioning techniques have prolonged battery lifespan, reducing maintenance requirements and increasing operational availability.
Power Management Strategies
Efficient power management is crucial for optimizing battery usage in nonnuclear submarines.
- Propulsion Prioritization:Power management systems prioritize propulsion needs, allocating sufficient energy to maintain desired speed and maneuverability.
- Auxiliary System Optimization:Non-essential auxiliary systems, such as lighting and ventilation, are managed to minimize power consumption.
- Energy Conservation Measures:Submarines employ energy-saving measures, such as reducing speed during low-power operations and using energy-efficient equipment.
Operational Considerations
Battery-powered submarines face unique operational considerations:
- Mission Duration:Mission duration is limited by battery capacity and power management strategies.
- Stealth Requirements:Battery charging requires surfacing or snorkeling, which may compromise stealth capabilities.
- Maintenance Schedules:Batteries require regular maintenance and replacement, impacting submarine availability.
Comparative Analysis: Nuclear vs. Nonnuclear Submarines
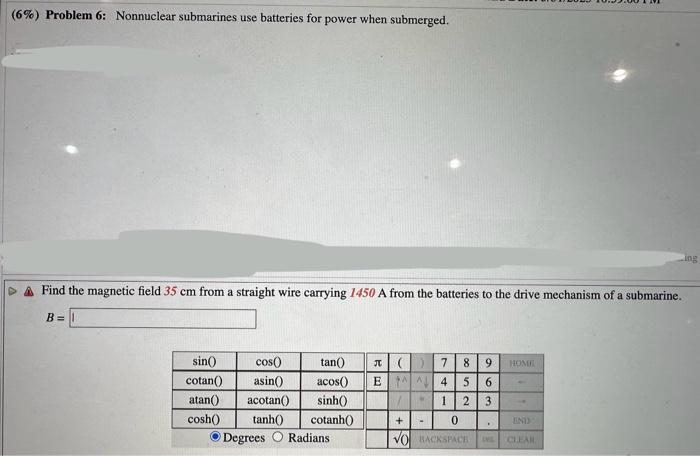
| Characteristic | Nuclear Submarines | Nonnuclear Submarines |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Nuclear reactor | Batteries |
| Endurance | Virtually unlimited | Limited by battery capacity |
| Range | Global | Regional |
| Environmental Impact | Potential for radioactive waste | No radioactive emissions |
Future Trends in Submarine Power Systems
Emerging technologies may shape the future of submarine power systems:
- Renewable Energy Sources:Integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wave energy, could supplement battery power.
- Energy Storage Advancements:Innovations in energy storage technologies, such as flow batteries and supercapacitors, could enhance energy density and efficiency.
- AI-Assisted Power Management:Artificial intelligence (AI) can optimize power management, predicting and adjusting energy consumption based on mission requirements.
FAQ Guide: Nonnuclear Submarines Use Batteries For Power When Submerged
What are the advantages of using batteries in nonnuclear submarines?
Batteries offer several advantages, including stealthier operations due to the absence of nuclear reactors, reduced maintenance requirements, and the ability to operate in shallow waters where nuclear submarines may face depth restrictions.
How long can nonnuclear submarines operate submerged on battery power?
The endurance of nonnuclear submarines on battery power varies depending on factors such as battery capacity, propulsion efficiency, and mission requirements. Typically, these submarines can remain submerged for several days to weeks.
Are batteries the only source of power for nonnuclear submarines?
No, nonnuclear submarines may also utilize diesel generators or air-independent propulsion systems to supplement or recharge their batteries while on the surface or at periscope depth.