Introduction to geospatial technology 6th edition – In the realm of geospatial technology, the sixth edition of “Introduction to Geospatial Technology” emerges as a comprehensive guide, illuminating the fundamentals, applications, and future prospects of this transformative field. With its in-depth exploration and engaging narrative, this text empowers readers to harness the power of location data, unlocking a world of possibilities.
As the field of geospatial technology continues to evolve rapidly, this latest edition provides a timely update, delving into emerging trends and cutting-edge advancements. From cloud computing and artificial intelligence to mobile GIS and data visualization, readers gain a comprehensive understanding of the latest innovations shaping the industry.
Overview of Geospatial Technology

Geospatial technology encompasses a wide range of tools and techniques used to collect, store, analyze, and visualize spatial data. It enables users to understand the relationships between geographic features and other attributes, making it a powerful tool for decision-making in various fields.
The field of geospatial technology has evolved significantly over the past few decades, with advancements in data acquisition, processing, and analysis capabilities. These advancements have made it possible to collect and analyze large and complex geospatial datasets, leading to new insights and applications.
Fundamental Concepts
Key concepts in geospatial technology include:
- Spatial data:Data that represents the location and attributes of geographic features.
- Geographic information systems (GIS):Software tools that allow users to create, manage, analyze, and visualize geospatial data.
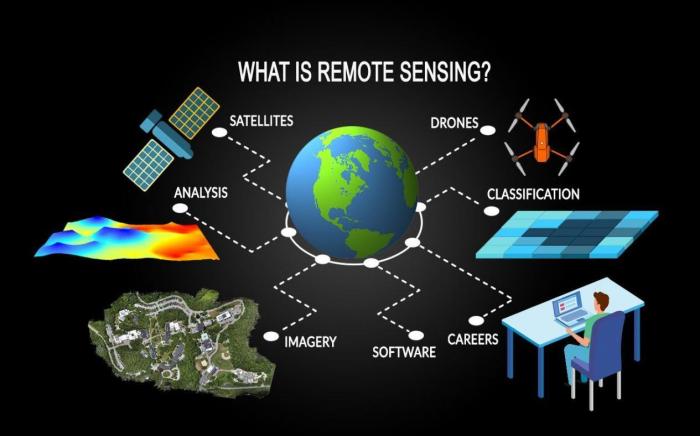
- Remote sensing:Techniques for acquiring data about the Earth’s surface from sensors mounted on satellites, aircraft, or drones.
Geospatial data can be classified into different types based on its dimensionality and geometry, such as points, lines, polygons, and rasters.
Data Acquisition and Processing
Geospatial data can be acquired through various methods, including:
- Field surveys:Collecting data directly in the field using tools such as GPS receivers and field notebooks.
- Remote sensing:Using sensors mounted on satellites, aircraft, or drones to capture data about the Earth’s surface.
- Data integration:Combining data from multiple sources to create a more comprehensive dataset.
Once data is acquired, it undergoes processing to prepare it for analysis. This may involve cleaning, transforming, and visualizing the data.
Geospatial Analysis and Modeling, Introduction to geospatial technology 6th edition
Geospatial analysis involves applying statistical and mathematical techniques to geospatial data to identify patterns and relationships. Common types of geospatial analysis include:
- Spatial statistics:Using statistical methods to analyze the spatial distribution of data.
- Spatial interpolation:Estimating values at unmeasured locations based on known values at nearby locations.
- Network analysis:Analyzing the relationships and connectivity between geographic features.
Geospatial models are mathematical representations of real-world phenomena that can be used to simulate and predict outcomes. Types of geospatial models include:
- Deterministic models:Models that produce the same output for the same input.
- Stochastic models:Models that produce probabilistic outputs based on random variables.
Applications of Geospatial Technology
Geospatial technology has a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Environmental management:Monitoring and managing natural resources, such as forests, water bodies, and wildlife.
- Urban planning:Designing and managing urban areas, including land use planning, transportation systems, and infrastructure.
- Transportation:Planning and managing transportation systems, including roads, railways, and airports.
Geospatial technology can provide valuable insights for decision-making in these fields by enabling users to visualize and analyze complex spatial data.
Emerging Trends and Future Directions
Emerging trends in geospatial technology include:
- Cloud computing:Using cloud-based platforms to store and process geospatial data.
- Artificial intelligence (AI):Using AI techniques to analyze and interpret geospatial data.
- Mobile GIS:Using mobile devices to collect and access geospatial data.
These trends are expected to drive future advancements in geospatial technology, leading to new applications and capabilities.
FAQ Guide: Introduction To Geospatial Technology 6th Edition
What is the scope of geospatial technology?
Geospatial technology encompasses the acquisition, processing, analysis, and visualization of geospatial data, providing insights into the spatial relationships and patterns of the real world.
What are the key concepts in geospatial technology?
Key concepts include spatial data, geographic information systems (GIS), remote sensing, and geospatial analysis, forming the foundation of the field.
What are the applications of geospatial technology?
Geospatial technology finds applications in diverse fields such as environmental management, urban planning, transportation, and public health, enabling data-driven decision-making and problem-solving.