AP Psychology States of Consciousness delves into the fascinating world of our conscious experiences, unveiling the diverse states of mind we traverse throughout our waking and sleeping hours. This exploration illuminates the neural mechanisms that govern these states and the profound impact they have on our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
From the depths of sleep to the altered realms of hypnosis and meditation, we embark on a journey that unravels the mysteries of consciousness, its functions, and its potential.
States of Consciousness

Consciousness refers to our subjective experience of the world around us and our internal thoughts and feelings. It encompasses a wide range of states, from wakefulness to sleep, and can be influenced by various factors such as drugs, meditation, and mental illness.
Neural Mechanisms of Consciousness
The neural mechanisms underlying consciousness are complex and still not fully understood. However, research suggests that several brain regions, including the brainstem, thalamus, and cerebral cortex, play a role in maintaining consciousness.
- Brainstem:The brainstem, particularly the reticular activating system (RAS), is responsible for maintaining wakefulness and arousal.
- Thalamus:The thalamus acts as a relay center for sensory information, filtering and directing it to the appropriate areas of the cortex.
- Cerebral Cortex:The cerebral cortex, especially the frontal lobes and parietal lobes, is involved in higher-order cognitive functions such as attention, perception, and decision-making, which are essential for conscious experience.
Altered States of Consciousness
Consciousness can be altered by a variety of factors, including:
- Drugs:Psychoactive drugs, such as alcohol, caffeine, and marijuana, can alter consciousness by affecting neurotransmitter systems in the brain.
- Meditation:Meditation practices, such as mindfulness meditation, can induce altered states of consciousness characterized by increased relaxation, focus, and awareness.
- Mental Illness:Disorders such as schizophrenia and depression can disrupt normal states of consciousness, leading to hallucinations, delusions, and other cognitive impairments.
Sleep and Dreaming

Sleep is a complex process that involves changes in brain activity, physiology, and behavior. It is essential for physical and mental health, and plays a crucial role in memory consolidation and other cognitive functions.Sleep is typically divided into two main types: rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep.
NREM sleep is further divided into three stages: N1, N2, and N3. Each stage of sleep is associated with specific brainwave patterns.
Stages of Sleep
N1 sleep is the lightest stage of sleep and is characterized by slow, rolling eye movements and muscle relaxation. Brainwaves during N1 sleep are primarily theta waves.N2 sleep is deeper than N1 sleep and is characterized by spindles and K-complexes on the EEG.
Spindles are bursts of high-frequency brainwaves, while K-complexes are large, slow waves.N3 sleep is the deepest stage of NREM sleep and is characterized by delta waves on the EEG. Delta waves are large, slow brainwaves.REM sleep is characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and vivid dreaming.
Brainwaves during REM sleep are similar to those seen during wakefulness.
Role of Sleep
Sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation, the process by which memories are strengthened and stored in the brain. Studies have shown that people who get a good night’s sleep are better able to remember information than those who do not.
Sleep also helps to improve attention, concentration, and problem-solving abilities.In addition to its role in memory and cognition, sleep is also essential for physical health. Sleep helps to repair tissues, boost the immune system, and regulate hormones. People who do not get enough sleep are more likely to experience health problems such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
Dreams
Dreams are vivid mental experiences that occur during REM sleep. The content of dreams can vary widely, from pleasant to frightening. Dreams are thought to serve a number of functions, including:* Processing emotions
- Solving problems
- Stimulating creativity
- Rehearsing for real-life situations
Altered States of Consciousness
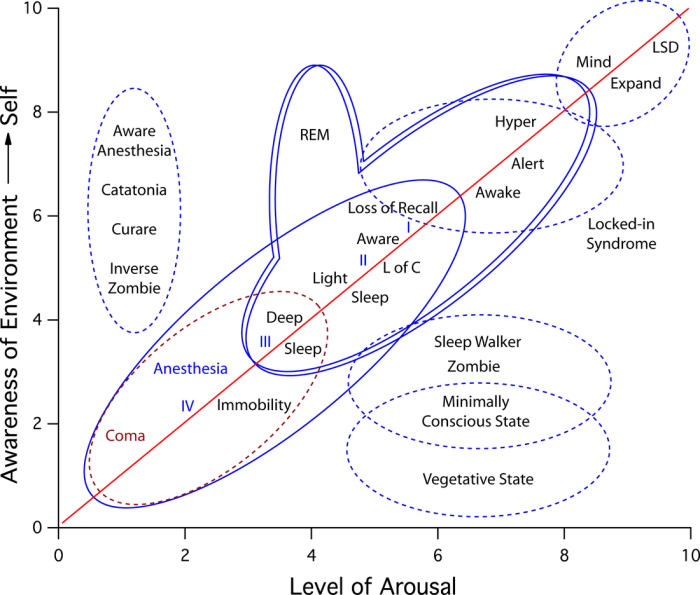
Altered states of consciousness (ASCs) refer to changes in the normal waking state that involve a shift in perception, awareness, and behavior. ASCs can be induced through various means, including meditation, hypnosis, drug use, and certain mental disorders.
Psychological and Physiological Changes
During ASCs, individuals experience psychological and physiological changes, such as:
- Cognitive changes:Altered perception, memory, and attention.
- Emotional changes:Heightened suggestibility, euphoria, or anxiety.
- Physiological changes:Changes in brain activity, heart rate, and respiration.
Potential Benefits and Risks
ASCs can offer potential benefits, such as:
- Therapeutic use:Meditation and hypnosis can help manage stress, anxiety, and pain.
- Spiritual growth:ASCs can facilitate mystical experiences and insights.
However, ASCs also carry potential risks, including:
- Negative psychological effects:Anxiety, panic attacks, or psychosis.
- Physical harm:Accidents or injuries due to impaired judgment.
- Addiction:Dependence on drugs or other substances that induce ASCs.
Hypnosis
Hypnosis is a state of focused attention and heightened suggestibility. It involves a narrowing of consciousness and an increased receptivity to suggestions. Individuals under hypnosis experience a range of physiological and psychological changes, including relaxation, reduced inhibitions, and enhanced imagination.
Hypnosis is typically induced through a process of guided relaxation and suggestion. The hypnotist uses verbal cues and techniques to help the individual enter a hypnotic trance. Hypnosis can be divided into several stages, each with varying degrees of suggestibility and responsiveness.
Stages of Hypnosis
- Light hypnosis:The individual is relaxed and focused but remains fully aware of their surroundings.
- Medium hypnosis:The individual becomes more deeply relaxed and responsive to suggestions, but they can still control their behavior.
- Deep hypnosis:The individual is highly suggestible and may experience amnesia for events that occur during hypnosis.
Theories of Hypnosis
There are several theories that attempt to explain how hypnosis works. Some of the most common theories include:
- Dissociation theory:This theory suggests that hypnosis involves a dissociation of the conscious and unconscious mind.
- Role-playing theory:This theory suggests that individuals in hypnosis are simply playing a role and pretending to be hypnotized.
- Social influence theory:This theory suggests that hypnosis is a form of social influence in which the hypnotist uses suggestion and persuasion to influence the individual’s behavior.
Uses of Hypnosis, Ap psychology states of consciousness
Hypnosis has a wide range of potential clinical uses, including:
- Pain management:Hypnosis can be used to reduce pain and discomfort during medical procedures or chronic pain conditions.
- Anxiety and stress reduction:Hypnosis can help individuals manage anxiety and stress, improve sleep, and reduce symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder.
- Smoking cessation and weight loss:Hypnosis can be used as an adjunct to other treatments for smoking cessation and weight loss.
Limitations of Hypnosis
While hypnosis can be an effective therapeutic tool, it also has certain limitations:
- Not everyone is susceptible to hypnosis:Some individuals are more resistant to hypnosis than others.
- Hypnosis is not a cure-all:Hypnosis should be used in conjunction with other treatments, and it is not a substitute for medical care.
- Hypnosis can be dangerous if used improperly:Hypnosis should only be performed by trained and experienced professionals.
Meditation and Mindfulness: Ap Psychology States Of Consciousness

Meditation is a practice that involves focusing one’s attention on a particular object, thought, or activity to train attention and awareness. Mindfulness is a type of meditation that involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment.There are many different types of meditation, each with its own unique benefits.
Some of the most common types of meditation include:
-
-*Mindfulness meditation
This type of meditation involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment. It can be practiced in many different ways, such as by focusing on the breath, the body, or thoughts and feelings.
-*Concentration meditation
This type of meditation involves focusing on a single object, such as a mantra, a candle flame, or the breath. It can help to improve focus and concentration.
-*Loving-kindness meditation
This type of meditation involves cultivating feelings of love and compassion towards oneself and others. It can help to reduce stress and promote well-being.
-*Transcendental meditation
This type of meditation involves using a mantra to focus the mind and achieve a state of deep relaxation. It can help to reduce stress and improve mental clarity.
Research has shown that meditation and mindfulness have a number of benefits, including:
-
-*Reduced stress and anxiety
Meditation and mindfulness have been shown to reduce stress and anxiety levels.
-*Improved sleep
Meditation and mindfulness can help to improve sleep quality and duration.
-*Increased focus and concentration
Meditation and mindfulness can help to improve focus and concentration.
-*Reduced pain
Meditation and mindfulness can help to reduce pain levels.
-*Improved emotional regulation
Meditation and mindfulness can help to improve emotional regulation and reduce emotional reactivity.
The neural mechanisms underlying meditation and mindfulness are still not fully understood, but research has shown that meditation and mindfulness can lead to changes in brain structure and function. These changes include:
-
-*Increased activity in the prefrontal cortex
The prefrontal cortex is involved in executive function, such as planning, decision-making, and attention. Meditation and mindfulness have been shown to increase activity in the prefrontal cortex, which may contribute to the improvements in focus and concentration that have been observed with meditation and mindfulness.
-*Decreased activity in the amygdala
The amygdala is involved in fear and anxiety. Meditation and mindfulness have been shown to decrease activity in the amygdala, which may contribute to the reductions in stress and anxiety that have been observed with meditation and mindfulness.
-*Increased connectivity between the prefrontal cortex and the amygdala
Meditation and mindfulness have been shown to increase connectivity between the prefrontal cortex and the amygdala. This increased connectivity may help to regulate the amygdala’s activity and reduce stress and anxiety.
There are many different ways to practice meditation and mindfulness. Some popular methods include:
-
-*Mindfulness meditation
To practice mindfulness meditation, simply sit in a comfortable position and focus your attention on your breath. Notice the rise and fall of your breath as you inhale and exhale. If your mind wanders, gently bring it back to your breath.
-*Concentration meditation
To practice concentration meditation, choose an object to focus on, such as a candle flame or a mantra. Sit in a comfortable position and focus your attention on the object. If your mind wanders, gently bring it back to the object.
-*Loving-kindness meditation
To practice loving-kindness meditation, sit in a comfortable position and close your eyes. Bring to mind someone you love and care about. Send them feelings of love and compassion. Gradually expand your circle of compassion to include all beings.
-*Transcendental meditation
To practice transcendental meditation, sit in a comfortable position and close your eyes. Repeat a mantra to yourself silently for 20 minutes. If your mind wanders, gently bring it back to the mantra.
Meditation and mindfulness are simple practices that can have a profound impact on your mental and physical health. If you are new to meditation and mindfulness, there are many resources available to help you get started. You can find books, articles, and websites on meditation and mindfulness, and you can also find meditation and mindfulness classes at many community centers and yoga studios.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the different states of consciousness?
AP Psychology recognizes various states of consciousness, including waking consciousness, sleep, dreaming, hypnosis, meditation, and altered states induced by drugs or other factors.
How does sleep contribute to our cognitive functioning?
Sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and overall cognitive health. Different stages of sleep are associated with specific brainwave patterns and serve distinct functions.
What are the potential benefits of altered states of consciousness?
Altered states of consciousness can provide therapeutic benefits, such as reducing stress, enhancing creativity, and promoting self-exploration. However, it’s important to approach these states with caution and under the guidance of trained professionals.
