Embark on a mathematical journey with area model and partial products, two powerful techniques that transform multiplication from a chore into a comprehensible concept. Dive into the world of grids and decompositions as we unveil the secrets of these remarkable methods.
Area model and partial products empower students to visualize and understand the underlying principles of multiplication, making it an accessible and enjoyable experience.
Area Model
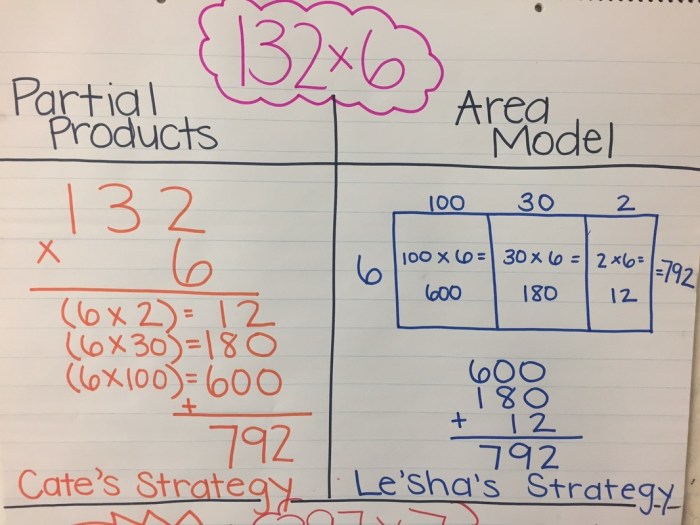
The area model is a visual representation of multiplication that helps students understand the concept of multiplying two numbers. It involves dividing a rectangle into smaller rectangles to represent the factors and their product.
Example
To multiply 3 x 4 using the area model, draw a rectangle with a length of 3 units and a width of 4 units. Divide the rectangle into 3 equal columns and 4 equal rows. The total number of small squares in the rectangle represents the product, which is 12.
Benefits
- Provides a concrete representation of multiplication, making it easier for students to understand the concept.
- Helps students visualize the relationship between the factors and the product.
- Can be used to solve multiplication problems involving larger numbers.
Limitations
- Can be time-consuming to draw the rectangles for larger multiplication problems.
- May not be suitable for all students, especially those with difficulty with spatial reasoning.
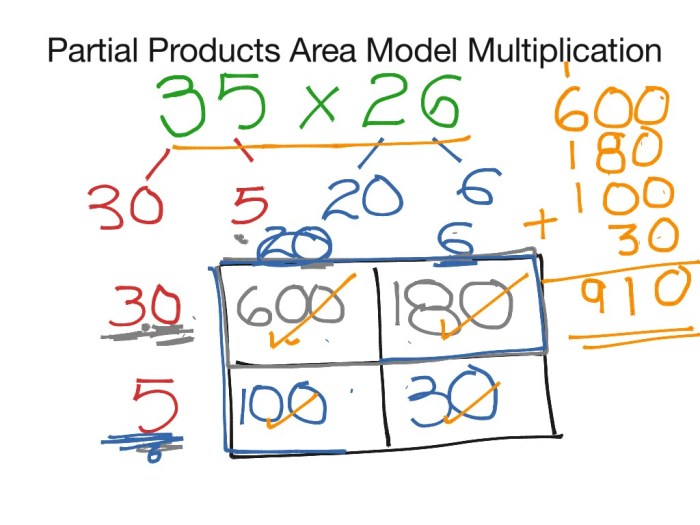
Partial Products
Partial products are a method for multiplying two numbers by breaking them down into their individual digits and multiplying those digits together. This method is particularly useful for multiplying large numbers or for students who are still learning the multiplication table.
Example
To multiply 123 by 45 using partial products, we first break down each number into its individual digits:
- 123 = 100 + 20 + 3
- 45 = 40 + 5
Next, we multiply each digit in the first number by each digit in the second number:
- 100 x 40 = 4000
- 100 x 5 = 500
- 20 x 40 = 800
- 20 x 5 = 100
- 3 x 40 = 120
- 3 x 5 = 15
Finally, we add up the partial products to get the final answer:
- 4000 + 500 + 800 + 100 + 120 + 15 = 5535
Therefore, 123 x 45 = 5535.
Area model and partial products are fundamental concepts in mathematics that provide a solid foundation for understanding multiplication. Just as joyas voladoras by brian doyle is a captivating tale that transports readers to a magical world, area model and partial products empower students to explore the realm of numbers with confidence and ease.
Benefits and Limitations
Partial products have several benefits:
- They are a simple and straightforward method for multiplying numbers.
- They can be used to multiply large numbers or numbers that are not easily multiplied using the traditional multiplication algorithm.
- They can help students to understand the concept of multiplication and how it works.
However, partial products also have some limitations:
- They can be time-consuming, especially for large numbers.
- They can be difficult to keep track of, especially if there are many partial products.
- They can be error-prone, especially if the numbers are large or if the student makes a mistake in multiplying the digits.
Overall, partial products are a useful method for multiplying numbers, but they should be used with caution and only when other methods are not practical.
Comparison of Area Model and Partial Products
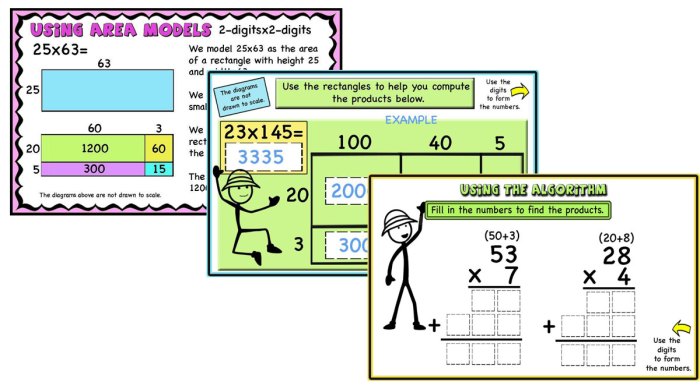
The area model and partial products are two methods for multiplying multi-digit numbers. Both methods involve breaking down the factors into smaller parts and then multiplying and adding the results. However, there are some key differences between the two methods.The
area model is a visual method that uses rectangles to represent the factors and the product. The length of each rectangle represents one of the factors, and the width represents the other factor. The area of the rectangle represents the product.For
example, to multiply 23 by 14 using the area model, we would draw a rectangle with a length of 23 and a width of 14. The area of the rectangle would be 322.The partial products method is an algorithmic method that involves multiplying each digit of one factor by each digit of the other factor and then adding the results.For
example, to multiply 23 by 14 using the partial products method, we would first multiply 2 by 14, which gives us 28. Then we would multiply 3 by 14, which gives us 42. Finally, we would add the two products together, which gives us 322.
Strengths and Weaknesses
The area model is a good method for visualizing the multiplication process. It is also a relatively easy method to understand and use. However, the area model can be difficult to use for multiplying large numbers.The partial products method is a more efficient method for multiplying large numbers.
It is also a more versatile method, as it can be used to multiply any two numbers, regardless of their size. However, the partial products method can be more difficult to understand and use than the area model.
Examples
Here are some examples of how the area model and partial products methods can be used to multiply multi-digit numbers:Area Model:To multiply 23 by 14 using the area model, we would draw a rectangle with a length of 23 and a width of 14. The area of the rectangle would be 322.Partial
Products:To multiply 23 by 14 using the partial products method, we would first multiply 2 by 14, which gives us 28. Then we would multiply 3 by 14, which gives us 42. Finally, we would add the two products together, which gives us 322.
Applications of Area Model and Partial Products
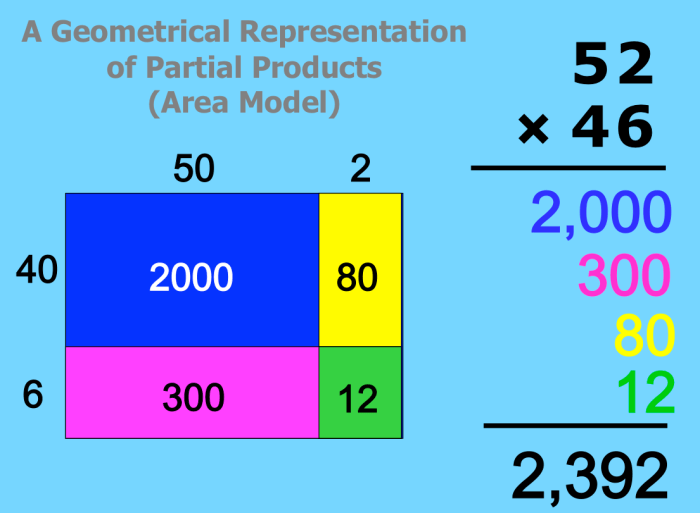
The area model and partial products are versatile tools that find applications in various real-world scenarios. These methods offer efficient and intuitive approaches to solving problems in diverse fields, including:
Everyday Life
- Grocery shopping:Calculating the total cost of groceries by multiplying the price of each item by its quantity.
- Home renovations:Estimating the area of a room to determine the amount of paint or flooring needed.
- Time management:Determining the total time spent on different tasks by multiplying the duration of each task by its frequency.
Education, Area model and partial products
- Multiplication and division:Teaching students multiplication and division concepts using visual representations.
- Geometry:Calculating the area of complex shapes by dividing them into rectangles and applying the area model.
- Statistics:Multiplying frequencies by probabilities to calculate expected values and probabilities.
Business and Finance
- Sales calculations:Multiplying the unit price of products by the quantity sold to calculate total sales.
- Budgeting:Estimating expenses and income by multiplying the cost or revenue per item by its frequency.
- Investment returns:Calculating the return on investments by multiplying the investment amount by the interest rate.
Science and Engineering
- Physics:Calculating the work done by a force by multiplying the force by the distance moved.
- Chemistry:Determining the concentration of a solution by multiplying the mass of solute by the volume of solution.
- Engineering:Calculating the area of cross-sections or surfaces of objects using the area model.
Extensions of Area Model and Partial Products
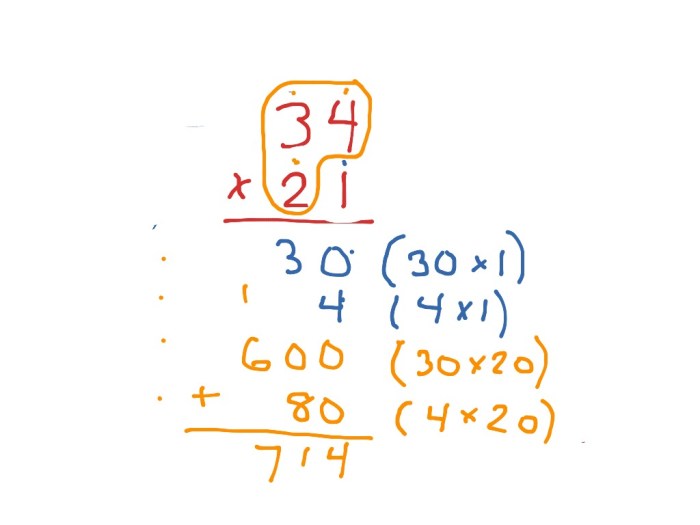
The area model and partial products methods provide a solid foundation for understanding multiplication. However, there are several extensions or variations of these methods that can be used to solve more complex multiplication problems.
Extending the Area Model
One extension of the area model is to use it to multiply three or more factors. This can be done by creating a larger rectangle and dividing it into smaller rectangles to represent each factor. For example, to multiply 123 by 45, we can create a rectangle with a length of 123 and a width of 45. We then divide the rectangle into smaller rectangles to represent the tens, ones, and hundredths of each factor.
Another extension of the area model is to use it to multiply decimals. This can be done by using a decimal grid. A decimal grid is a grid with 10 rows and 10 columns. Each row represents a power of 10, and each column represents a digit.
To multiply two decimals, we can place each decimal in a row of the grid and then multiply the digits in each column. The product will be the sum of the products in each column.
Extending Partial Products
One extension of partial products is to use it to multiply three or more factors. This can be done by multiplying each factor by the product of the other two factors. For example, to multiply 123 by 456, we can multiply 123 by 45 and then multiply the product by 6. This gives us a product of 696,780.
Another extension of partial products is to use it to multiply decimals. This can be done by multiplying each decimal by the product of the other two decimals. For example, to multiply 12.3 by 45.6, we can multiply 12.3 by 45 and then multiply the product by 6. This gives us a product of 6967.8.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the area model?
The area model represents multiplication as the area of a rectangle, with the factors as the length and width.
How do I use partial products?
Partial products involve multiplying individual digits of the factors and then adding the results.
Which method is better, area model or partial products?
Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages. The area model is more visual, while partial products may be easier for larger numbers.